Apps which integrate push or local notifications can customise notifications on Apple Watch. Let’s go through steps required for adding dynamic notifications on Apple Watch. Sample use case is an app which reminds when a plant needs watering. We’ll only concentrate on adding dynamic notification view and leave out sending local notifications from the iOS app.
Adding build target for rich notifications on Apple Watch
If Apple Watch app does not exist in the project the first step is to add it. In Xcode, we’ll add a new build target and configure it to include notification scene. In Xcode, open new target view: File>Target and select Watch App for iOS App template.

Make sure SwiftUI is selected in the user interface selection and “Include Notification Scene” is also selected. We’ll embed it in the companion app so make sure current iOS app target is set to “Embed in Companion App”. As a side note, since iOS 13 and WatchOS 6, Apple Watch apps can be independent as well.

Click on Finish and then Xcode will ask about activating the new scheme, click on active. It will just select the new target and we can build it right away. When inspecting the project, Xcode added two targets: watch app and extension. App contains storyboard and extension contains all the code. Storyboard is wired up so that the scene displays HostingController which is WKHostingController subclass and is responsible of hosting your SwiftUI view in the Apple Watch app. In addition, there are scenes for static and dynamic notifications. We are interested in creating dynamic notifications and in the Storyboard we can see that the dynamic view is provided by NotificationController (subclass of WKUserNotificationHostingController) which hosts SwiftUI view for the notification. There we can provide the custom interface for our user notification. Dynamic notification view is selected if the notification category matches with the one defined in the Storyboard.
If you need more information how to set up Xcode project please check: “Setting Up a watchOS Project”.
Parsing notification payload and setting up dynamic notification view
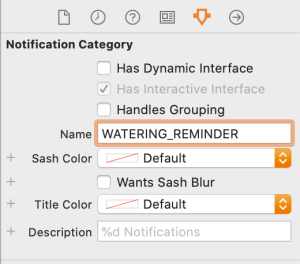
NotificationController’s responsibility is to consume user notification’s payload and configuring the SwiftUI view with it. User notification is provided by didReceive function and there we can extract the information needed for showing the view. When it comes to locally testing the dynamic view, we can add required data to the PushNotificationPayload.apns file. As we show information about plants, let’s add example plant object to the file. Also, we change category to something meaningful. Make sure to update Storyboard when setting new category.
{
"aps": {
"alert": {
"body": "Test message",
"title": "Optional title",
"subtitle": "Optional subtitle"
},
"category": "WATERING_REMINDER",
"thread-id": "plantid123"
},
"plant": {
"id": "plantid123",
"name": "Aloe",
"lastDate": 1579937802,
"nextDate": 1580515200
}
}
Plant related information is available when accessing UNNotification’s request.content.userInfo. We can use Decodable and JSONDecoder for converting Dictionary representing the plant into value type. As JSONDecoder requires JSON data then we can first use JSONSerialization and then passing the JSON data to JSONDecoder. Alternatively we could also manually read values from the userInfo dictionary and then creating the value type. Note that we use view model for providing data to SwiftUI view and not the Plant type directly.
struct Plant: Decodable {
let id: String
let name: String
let lastDate: Date
let nextDate: Date
}
do {
let plantInfo = notification.request.content.userInfo["plant"] as! [String: Any]
let data = try JSONSerialization.data(withJSONObject: plantInfo, options: [])
let decoder = JSONDecoder()
decoder.dateDecodingStrategy = .secondsSince1970
let plant = try decoder.decode(Plant.self, from: data)
viewModel = NotificationViewModel(plant: plant)
}
catch let nsError as NSError {
print(nsError.localizedDescription)
}
In addition, we would like to add 3 actions user can take: marking the plant as watered, deferring the reminder for couple of hours, or scheduling it for tomorrow. Actions are represented with instances of UNNotificationAction and when user taps on any of those, UNUserNotificationCenter’s delegate method is called with the identifier in the companion iOS app (userNotificationCenter(_:didReceive:withCompletionHandler:)).
let doneTitle = NSLocalizedString("NotificationAction_Done", comment: "Done button title in notification.")
let laterTitle = NSLocalizedString("NotificationAction_Later", comment: "Later button title in notification.")
let tomorrowTitle = NSLocalizedString("NotificationAction_Tomorrow", comment: "Tomorrow button title in notification.")
notificationActions = [
UNNotificationAction(identifier: "water_done", title: doneTitle, options: []),
UNNotificationAction(identifier: "water_later", title: laterTitle, options: []),
UNNotificationAction(identifier: "water_tomorrow", title: tomorrowTitle, options: [])
]
The full implementation of the NotificationController becomes like this (including the creation of SwiftUI):
final class NotificationController: WKUserNotificationHostingController<NotificationView> {
private var viewModel: NotificationViewModel?
override var body: NotificationView {
return NotificationView(viewModel: viewModel!)
}
override func didReceive(_ notification: UNNotification) {
do {
let plantInfo = notification.request.content.userInfo["plant"] as! [String: Any]
let data = try JSONSerialization.data(withJSONObject: plantInfo, options: [])
let decoder = JSONDecoder()
decoder.dateDecodingStrategy = .secondsSince1970
let plant = try decoder.decode(Plant.self, from: data)
viewModel = NotificationViewModel(plant: plant)
}
catch let nsError as NSError {
print(nsError.localizedDescription)
}
let doneTitle = NSLocalizedString("NotificationAction_Done", comment: "Done button title in notification.")
let laterTitle = NSLocalizedString("NotificationAction_Later", comment: "Later button title in notification.")
let tomorrowTitle = NSLocalizedString("NotificationAction_Tomorrow", comment: "Tomorrow button title in notification.")
notificationActions = [
UNNotificationAction(identifier: "water_done", title: doneTitle, options: []),
UNNotificationAction(identifier: "water_later", title: laterTitle, options: []),
UNNotificationAction(identifier: "water_tomorrow", title: tomorrowTitle, options: [])
]
}
}
NotificationView presenting the dynamic notification
Previously mentioned view model NotificationViewModel provides text for NotificationView and it looks pretty simple, mainly dealing with creating strings with formatted dates. As we only want to show day and month then we need to create dateFormat using current locale.
struct NotificationViewModel {
private let plant: Plant
init(plant: Plant) {
self.plant = plant
}
var title: String {
return plant.name
}
var subtitle: String {
return NSLocalizedString("NotificationView_Subtitle", comment: "Notification suggestion text")
}
private let dateFormatter: DateFormatter = {
let formatter = DateFormatter()
formatter.dateFormat = DateFormatter.dateFormat(fromTemplate: "dMMMM", options: 0, locale: .current)
return formatter
}()
var lastWatering: String {
let format = NSLocalizedString("NotificationView_LastWatering", comment: "Last watering date.")
return String(format: format, dateFormatter.string(from: plant.lastDate))
}
var nextWatering: String {
let format = NSLocalizedString("NotificationView_NextWatering", comment: "Next watering date.")
return String(format: format, dateFormatter.string(from: plant.nextDate))
}
}
SwiftUI view is also pretty simple with containing 4 text labels and one divider.
struct NotificationView: View {
let viewModel: NotificationViewModel
var body: some View {
VStack {
Text(viewModel.title).font(.title)
Text(viewModel.subtitle).font(.subheadline)
Divider()
Text(viewModel.lastWatering).font(.body).multilineTextAlignment(.center)
Text(viewModel.nextWatering).font(.body).multilineTextAlignment(.center)
}
}
}


Summary
We added Apple Watch app to an existing iOS app and implemented dynamic notification view for one notification category. We looked into how to parse data associated with the user notification, create SwiftUI view and add action buttons. Next steps would be to handle notification actions in the companion iOS app based on the notification button identifier.
If this was helpful, please let me know on Mastodon@toomasvahter or Twitter @toomasvahter. Feel free to subscribe to RSS feed. Thank you for reading.
Example project
WaterMyPlants (GitHub)


